How Do You Know Which Histogram Best Represents Data
The lower the bar the lower the frequency of data. If you want to see the development of data within your chart histograms will be your choiceIn a histogram the horizontal axis shows frequency and vertically you can see the interval or time range values.

I O Graphs Https Github Com Khailey Fio Scripts Graphing Visual Display Histogram
Place evenly spaced marks along this line that correspond to the classes.

. The thick black dashes indicate data points that contribute to the histogram left and density curve right. The best answer is that a histogram measures distribution of continuous data. Weight height how much time etc.
First identify all the different values found in Viewgraph 6 -160 -010. The higher the bar the higher the frequency of the data. In fact the shape of a histogram is something you should always note when evaluating the data the histogram represents.
Identify the peaks which are the tallest clusters of bars. Bins are also sometimes called intervals classes or buckets. The most obvious way to tell if a distribution is approximately normal is to look at the histogram itself.
Choose the scale on the vertical axis while drawing a histogram check for the highest number that divides all the frequencies. So asymmetric distribution is a data distribution where one of the two halves appears as a mirror image of another half. When the data are skewed to the right the mean value is larger than the median of the data set.
Step 1. You need to summarize your data to make it easy to interpret. A histogram displays numerical data by grouping data into bins of equal width.
A histogram is a special type of bar chart. To construct a histogram from a continuous variable you first need to split the data into intervals called bins. Each bin is plotted as a bar whose height corresponds to how many data points are in that bin.
Assess the spread of your sample to understand how much your data varies. This way you can get a picture of data distribution and you can clearly see the outliers in your set of data. For the above data set the frequencies in each bin.
But when the data is in categories such as Country or Favorite Movie we should use a Bar Chart. The mode is the data value that occurs the most often in a data set. Both graphs employ vertical bars to represent data.
The data spread is from about 2 minutes to 12 minutes. You can do this by constructing a tally sheet. For a symmetric histogram the values of the mean median and mode are all the same and are all.
The two side looks the same if the histogram is folding in between. From a glance youll immediately see whether you had equal distribution or not. A histogram is a graph that is used to summarise continuous data.
The height of a bar corresponds to the relative frequency of the amount of data in the class. One look and youll know how the data is spread among the ranges. This can be found under the Data tab as Data Analysis.
As for when the center is the mean then standard deviation should be used since it measure the distance between a data point and the mean. What does it mean when a histogram is positively skewed. Count the number of values that fall into each bin.
For example in the following histogram of customer wait times the peak of the data occurs at about 6 minutes. If there is no such number exists then check for the highest number that divides most of the frequencies. Start by putting all of your values in ascending order.
Label the marks so that the scale is clear and give a name to the horizontal axis. If the graph is approximately bell-shaped and symmetric about the mean you can usually assume normality. The range of each bar is also called the Class Interval In the example above each class interval is 05 Histograms are a great way to show results of continuous data such as.
The peaks represent the most common values. This number is the frequency of each range. How do you find unusual values in a histogram.
Once you have chosen your bins you need to order and sort the data into these bins. In the example above age has been split into bins with each bin representing a 10-year period starting at 20 years. Draw a vertical line just to the left of the lowest class.
Histograms are a great way to verify the equality of data points distribution. Organize these values from smallest to largest -180 -120. When it is skewed right or left with high or low outliers then the median is better to use to find the center.
Then draw a line at the division of the bins. In a histogram if they have the same shape on both sides of the medium the data are symmetric. The normal probability plot is a graphical technique for normality testing.
The best measure of spread when the median is the center is the IQR. The highest peak of the histogram represents the location of the mode of the data set. Step 2 - Summarize your data on a tally sheet.
Data Spread Basically the bars in a histogram represents the data points belonging to that range. Note how each point contributes a small bell-shaped curve to the overall shape. In this example the ranges should be.
Separate the data into the bins. Each bin contains the number of occurrences of scores in the data set that are contained within that bin. Reading a histogram The heights of the bars tell us how many data points are in each bin.
At first glance histograms look very similar to bar graphs. Choose a scale for the vertical axis that will accommodate the class with the highest frequency. Box plot and violin plot.
It can be used to display variation in weight but can also be used to look at other variables such as size time or temperature. A histogram is skewed to the right if most of the data values are on the left side of the histogram and a histogram tail is skewed to right. With right-skewed distribution also known as positively skewed distribution most data falls to the right or positive side of the graphs peak.
But looks can be deceiving. Open the Data Analysis box. Enter the relevant input range and bin range.

Using Histograms To Understand Your Data Statistics By Jim

Tqm And Quality Control Processes Process Control Statistical Process Control Change Management

Histogram In 7 Qc Tools Histogram Process Improvement Correlation Graph

Histogram Graph Definition Properties Examples

Histogram Graph Definition Properties Examples

How To Make A Histogram Your Audience Will Understand

Statistics Resources Cazoom Maths Worksheets Histogram Worksheet Printable Math Worksheets Histogram

Types Of Graphs Posters Types Of Graphs Graphing Line Graphs

Histogram Definition Thank You Jenny Eather Dictionary For Kids Math Blog Histogram

Histogram Graph Definition Properties Examples

Histogram Graph Definition Properties Examples
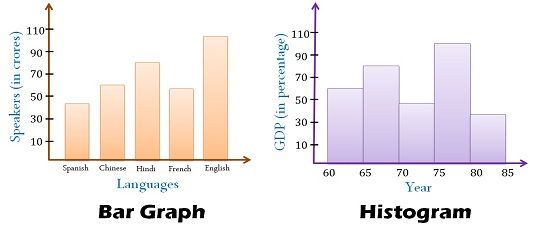
Difference Between Histogram And Bar Graph With Comparison Chart Key Differences

2011 S1 09 Maths Blog Data Handling Histogram Math Blog Math Histogram

Bar Graph And Histogram Foldable Bar Graphs Graphing Foldables

Using Histograms To Understand Your Data Statistics By Jim

Histogram Graph Definition Properties Examples


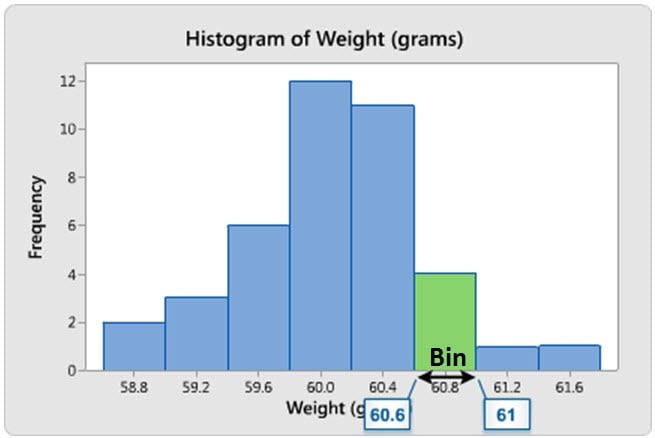
Comments
Post a Comment